BEST foods to eat after a workout – tips from the Martin Coaching Team
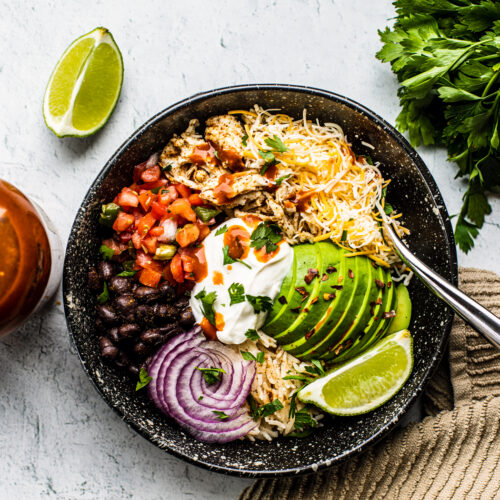

Foods consumed after a workout will impact recovery and sports performance.
We asked the Martin coaching team about which foods they eat after a workout and it was no surprise that we received great responses instantly. At the elite level, nutrition is dialed in and the athletes know which foods to grab after a tough workout to promote recovery.
QUICK AND HEALTHY LUNCH IDEAS FOR COLLEGE STUDENTS
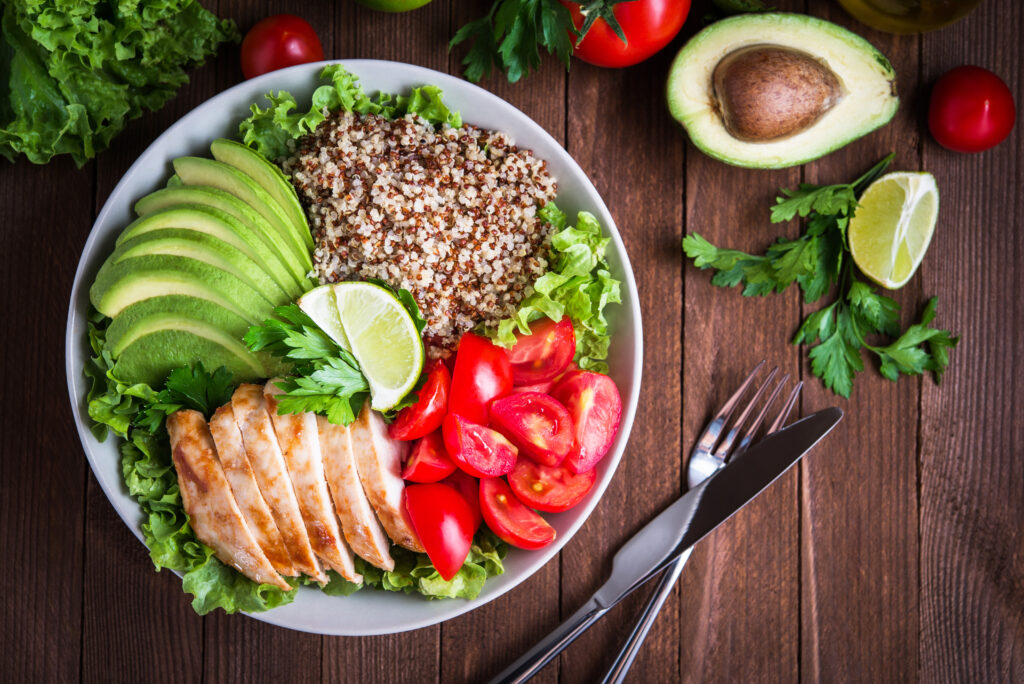

Eating a balanced lunch offers numerous physical, mental, and emotional benefits, making it especially crucial for college athletes. However, research shows that up to 60% of college students skip lunch due to their busy schedules and budget (Pendergast, 2016). Skipping this meal can negatively impact energy, hunger management, and overall well-being.
Body Composition Testing: When is it Helpful and When is it Harmful?

TW: This content mentions eating disorders and body image.
Body composition testing offers a window into the intricate components that constitute our bodies. It surpasses simple weight measurements by evaluating the distribution and proportion of tissues like fat mass, muscle mass, and bone density, providing a detailed profile of physical makeup.
TOP FUELING OPTIONS FOR ENDURANCE ATHELTES
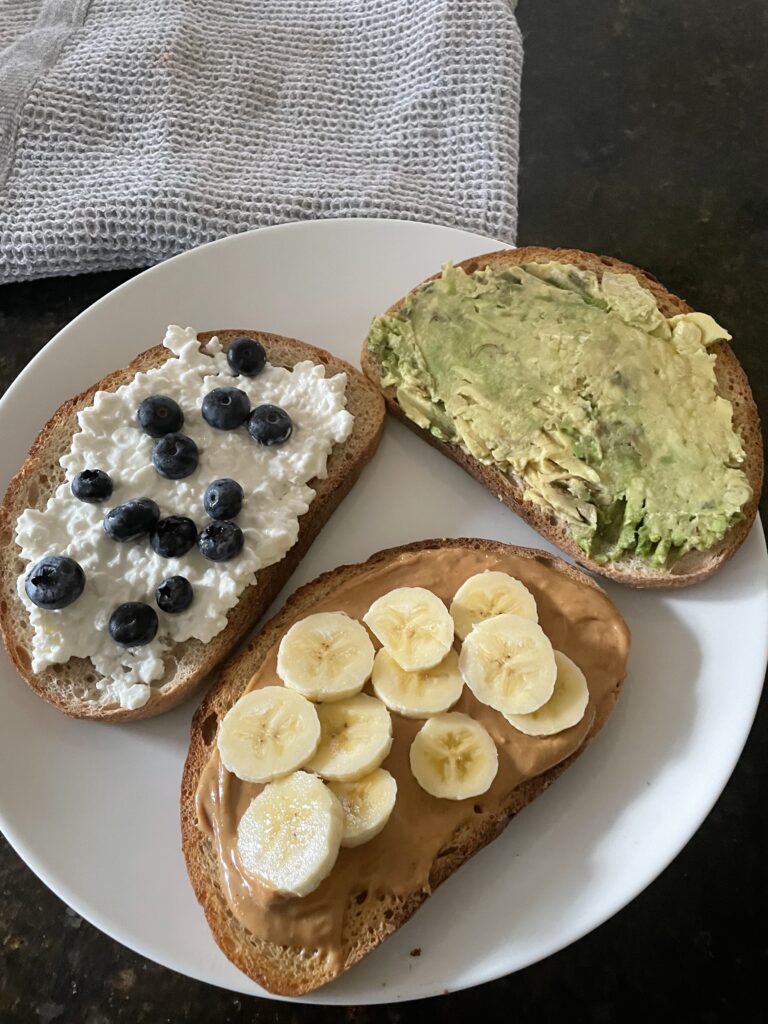

Here’s a list of the best fueling options for endurance athletes—designed to support energy, facilitate recovery, and keep performance strong. These snacks are easy to digest and perfect for on-the-go fueling. Keep them handy to stay energized throughout your day and training.
EATING DISORDER OR RED-S? THE KEY DIFFERENCES

TW: This content mentions eating disorders and body image.
Eating disorders are mental health conditions, whereas RED-S (Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport) is a physiological state caused by an energy imbalance. However, these conditions can overlap.
Winter Supplements for Runners

Winter months bring unique nutritional needs for runners, including reduced sunlight exposure, which increases the need for Vitamin D. Meeting nutrition goals through food is ideal, but supplements can be helpful when dietary intake is insufficient. Below are recommended winter supplements and their top food sources.
Should Athletes Use a CGM? A Look at the Benefits and Drawbacks
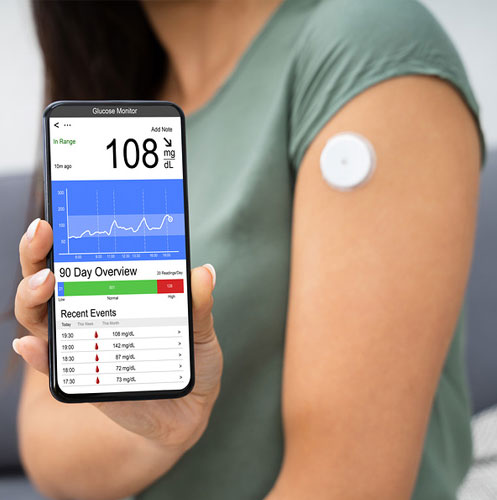
A Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) is a medical device designed to deliver real-time measurements of glucose (sugar) levels in the body. Although it is mainly utilized by individuals with diabetes to regulate their blood sugar, it has also become increasingly popular among athletes and health enthusiasts. While these devices offer a wealth of data, it’s crucial to consider how that information will be applied effectively.
Don’t Wait: Understanding Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) and Low Energy Availability (LEA)

By Kate Cochran, Nutrition Intern, NYU Track and Field
When I first learned about low energy availability (LEA) and relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) at twenty-one, I was four years deep into my distance running journey. It was while reading “How She Did It” by renowned female distance athletes Molly Huddle and Sara Slattery, both esteemed Olympians themselves, where I first learned about the syndrome. It was something I wish I knew when I began running at sixteen. I firmly believe it’s essential for every female athlete to familiarize themselves with RED-S early on, considering its potential impact on their athletic path.
Conversations with Rachel Kaplan, Division 1 College Gymnast
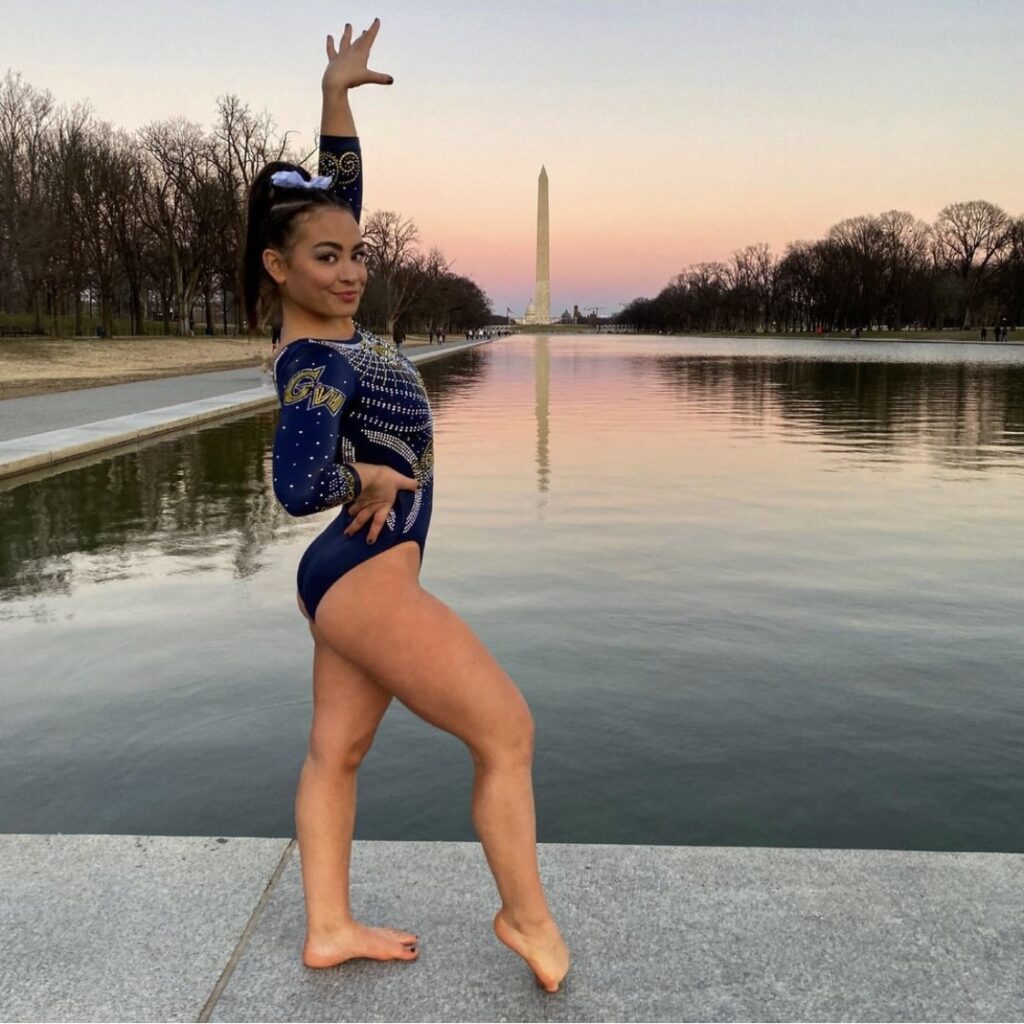

I had the opportunity to watch the Olympic gymnastics with my niece, Rachel Kaplan, a Division 1 gymnast and uneven bar specialist. Here are some key excerpts from our conversation that can be valuable for anyone looking to compete in college, especially females in body image-focused sports:
Optimizing Performance: Nutrition Strategies for a Soccer Game
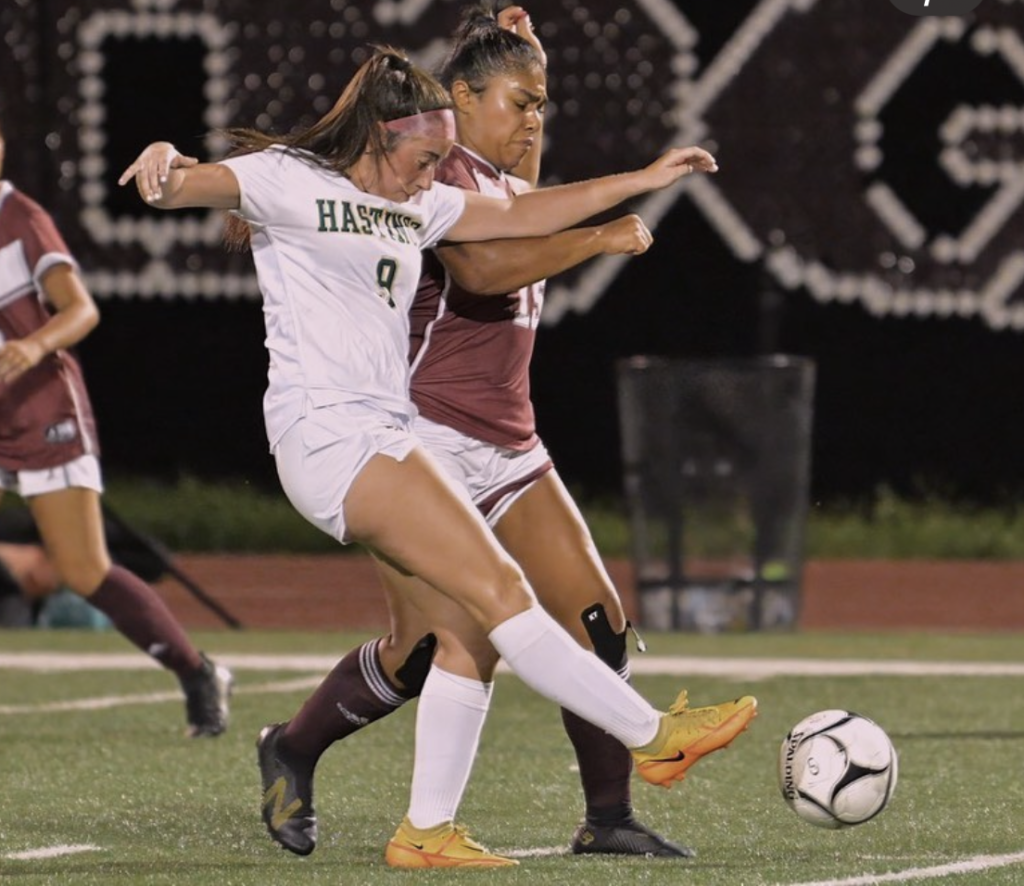

Soccer is an endurance sport that requires a steady supply of nutrients. Optimizing energy levels and performance involves special attention to fueling strategies before, during and after training and competing. In order to keep up with high energy and fluid requirements, special attention needs to focus on practices, games and tournaments.